 |
 |
- Search
| J. People Plants Environ > Volume 23(4); 2020 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background and objective: Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) are commonly used as a deicing agent in South Korea and penetrate the soil on the roadside, causing damage to plants. This study was conducted to investigate the salinity reduction effect of Pennisetum alopecuroides and the chemical characteristics of soil leachate.
Methods: The plants were treated with five different concentrations of CaCl2 (0, 1, 2, 5, and 10g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1) and were grouped into the Cont., C1, C2, C5, and C10 groups. CaCl2 of 200 m ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 was sprayed to each plant once every two weeks. The growth of P. alopecuroides (plant height, leaf length, leaf width and the number of leaves) was measured. The level of EC and pH, and exchangeable cations (K+, Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+) in the leachate of soil was monitored.
Results: The pH of soil leachate decreased as the CaCl2 concentration increased, and the EC increased significantly. The content of K+ did not change significantly until the concentration of CaCl2 reached 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, but the content of Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+ significantly increased. The plant height, leaf length, and leaf width of P. alopecuroides showed the highest value in CaCl2 1g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 followed by CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 and the control group. Root fresh weight was the highest in CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1. On the other hand, there was no change in the shoot fresh weight, dry weight and root dry weight, and P. alopecuroides growth inhibition at the concentration of 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 or higher in the plant height and leaf length.
Conclusion: P. alopecuroides is relatively highly salt-tolerant and can improve the salt damaged soil by lowering the content of the salt-based exchangeable K+ ions.
Methods: The plants were treated with five different concentrations of CaCl2 (0, 1, 2, 5, and 10g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1) and were grouped into the Cont., C1, C2, C5, and C10 groups. CaCl2 of 200 m ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 was sprayed to each plant once every two weeks. The growth of P. alopecuroides (plant height, leaf length, leaf width and the number of leaves) was measured. The level of EC and pH, and exchangeable cations (K+, Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+) in the leachate of soil was monitored.
Results: The pH of soil leachate decreased as the CaCl2 concentration increased, and the EC increased significantly. The content of K+ did not change significantly until the concentration of CaCl2 reached 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, but the content of Ca2+, Na+, and Mg2+ significantly increased. The plant height, leaf length, and leaf width of P. alopecuroides showed the highest value in CaCl2 1g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 followed by CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 and the control group. Root fresh weight was the highest in CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1. On the other hand, there was no change in the shoot fresh weight, dry weight and root dry weight, and P. alopecuroides growth inhibition at the concentration of 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 or higher in the plant height and leaf length.
Conclusion: P. alopecuroides is relatively highly salt-tolerant and can improve the salt damaged soil by lowering the content of the salt-based exchangeable K+ ions.
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) are commonly used as a deicing material to prevent heavy snow from freezing to roads, and deicing materials are sprayed to roads in Korea mostly using a pre-wetted salt spreading method (Lee et al., 2007). Using the method, salt is pre-wetted with calcium chloride solution (30%) at the weight ratio of 7:3 before spraying it to roads to improve its snow melting performance by combining the rapid snow removing (quick acting) effect of calcium chloride solution with the continuity of sodium chloride (Cho, 2003). Compared to conventional snow removing methods, however, this method requires three times more calcium chloride, and chlorides on the roadside easily infiltrate into soil and aggravate damage to plants (Park and Bang, 2015). Salinity affects the body of plants largely in two ways: one is reducing soil water potential and the other is causing metabolic disorders with certain saline ions excessively accumulated within the body of plants (Shim et al., 1998). In particular, the excessive concentration of salt in soil acts as a more serious stressor in dry soil and inhibits the growth and development of plants (Beak et al., 2014). In addition, salt damage to plants includes a decrease in the content of chlorophyll, inhibited growth and photosynthesis and withering (Shim et al., 2012), and depending on the concentration and lasting time of salt, changes are caused in various physiological metabolism processes and inhibit the growth of plants (Gupta and Huang, 2014). To address these problems, low-chloride deicing materials (salt mixed with organic acid) were developed, but they reduced damage from chlorides but also the performance of snow removing (Shin et al., 2001).
Greening of artificial ground such as the roadside not only secures green spaces but also solves various urban environmental problems and contributes to improving the quality of life for urban residents (Jeong et al., 2020). Herbaceous plants are suitable for the climate and natural features of Korea and have great adaptability, and thus can be regenerated and managed easily as a stable vegetation structure (Jeong et al., 2001). Moreover, they have excellent ornamental value in leaves, flowers and thus their utility value is increasing as gardening and landscaping plants (Jeong et al., 2020). Recently, studies have been conducted on the development of plant materials that can reduce salinity in soil on the roadside or improve growth environments using salt tolerant plants (Ju et al., 2019). Limonium tetragenum, Atriplex triangularis, Echinochloa crus-galli var, Sesbania rostrata and Cynodon dactylon L. were selected as a species applicable for the restoration of plants in the soil of reclaimed lands (Lee et al., 2007) and it was also reported that plants including Carex blepharicarpa, Carex matsumurae, Carex lenta and Iris pseudoacorus L. can be utilized in salt-damaged lands as they can tolerate the high concentration of salt in the soil (Shim et al., 2012). Plants sense external stressors and activate their defense genes, having environmental stress adaptation systems such as ion homeostasis, osmotic compensation and injury repair (Yun, 2005). Plant leaves also play a role as a biofilter, and are known to be effective in removing heavy metals (mercury, lead), sulfur dioxide, hydrogen fluoride (HF), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particular matter (PM) in the air (Kim et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2012; Son et al., 2019). Salt tolerant plants absorb salt in the soil and accumulate it in their body, serving as a biological pump (Lee et al., 2007). For this reason, salt tolerant plants can be utilized as a good resource for improving the soil environment of salt-damaged lands. Pennisetum alopecuroides, as a perennial poaceous herb, has well-developed roots and thus is widely used to maintain and stabilize lands, and it has been utilized to prevent and manage the disturbance of ecosystems and the destruction of natural landscapes when greening the slopes of roads in Korea (Dang et al., 2017). In addition, it is known to grow stably and purify non-point pollution sources in water (Lee et al., 2015).
In order to reduce salt in the soil of the roadside damaged by calcium chloride contained in deicing materials, this study aimed to identify the tolerance of Pennisetum alopecuroides to salt, to examine physicochemical changes in the leachate of the soil and thus to assess the applicability of Pennisetum alopecuroides as a plant material for reducing salinity in the soil damaged by deicing materials.
This study was conducted in a green house in the Glocal Campus of Konkuk University located in Chungju, Chungcheongbuk-do from April to October, 2018. The average temperature inside the green house during the experiment was maintained at 19.88 ┬░C and the total of the average duration of daily sunshine was 248.9 hr. The soil used in this study was light-weight gardening topsoil (Hanpanseung, SGtech, Korea) mixed with coco peat 74.84%, vermiculite 15%, biotite 5%, perlite 5%, fertilizer 0.158%, and wetting agent 0.002% in order to minimize soil-related variables other than the treatment of calcium chloride. Pennisetum alopecuroides used as an experimental plant was purchased from a botanical garden located in Cheonan, Chungcheongnam-do in March, 2018, Seedlings of which plant length was 10ŌĆō12 cm and root length was 2ŌĆō3 cm were purchased and were placed within the green house for acclimatation for about one month. After that, their length was uniformly cut to be 5 cm before using them in this study. The deicing material used in this study was the calcium chloride powder (CaCl2, Oriental chemical Industries., Korea) with a purity of 74% used in the pre-wetted salt spreading method. Its concentration was set to be 0, 1, 2, 5 and 10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 and the experimental group was treated with it.
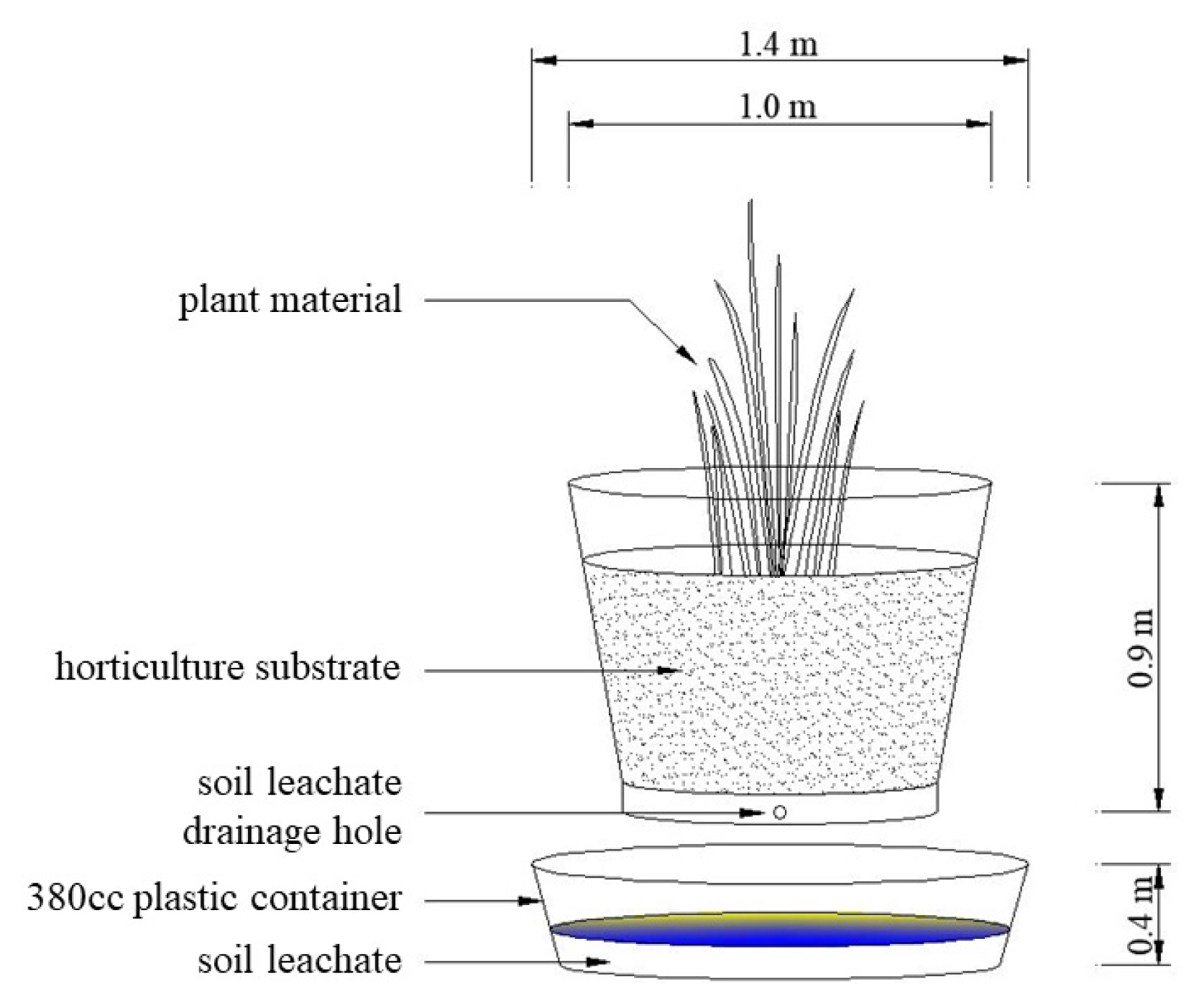
To examine the growth of Pennisetum alopecuroides and the characteristics of the leachate of soil depending on the concentration of calcium chloride, one seedling was planted in a 4-inch (0.11m ├Ś 0.9m) plastic pot with a felt piece placed on its bottom and filled with 100 g of the gardening topsoil. The process was repeated 10 times and the plants were completely randomly assigned. Referring to the concentration range of salt when a deicing material directly contacts snow (0.87ŌĆō5%; Shin et al., 2010), five calcium chloride solutions were prepared as follows: not-treated, 1, 2, 5 and 10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (Cont., C1, C2, C5, C10 groups respectively), and when plants were stabilized after about 10 days of acclimatation, the prepared calcium chloride solutions were sprayed to their respective groups (200 m ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 for one time) at an interval of two weeks. The soil leachate drained from the bottom of the pots was collected using a 1.4 m-diameter plastic container placed below the pots (Fig. 1), and during the experimental period the plants were watered for their basic growth. The collected soil leachate was filtered using 5D filter paper (Adventec, filter paper No. 5B, Japan) and its electrical conductivity (ST-3100C, Ohaus Crop, USA) and acidity (ST-3100pH, Ohaus Corp, USA) were measured, and to examine changes in exchangeable cations of salt in the soil depending on the concentration of calcium chloride, K+, Ca2+, Na+ and Mg2+ were analyzed using an inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP OES DV-5300, Perkin elmer, USA). The elevation of the setting for testing the leachate drained from the soil was as shown in Fig. 1. The growth response of Pennisetum alopecuroides to different calcium chloride concentrations was analyzed by measuring the height of plants and the length, width and number of leaves in August when it grows most actively. After completing this experiment, the plants used in this study were collected to measure the fresh weight of the aerial part and underground part. After that, they were dried in a dry oven (C-DF, CHANGSHIN Sci CO, Korea) for 48 hours until there was no moisture left and their dry weight was measured.
The collected data were analyzed using SPSS 25.0 (IBM, New York, USA), and significance between treatment means at the significance level of 5% was tested through DuncanŌĆÖs multiple range test. Graphs were created using SigmaPlot 12.3 (Systat software, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA).
The characteristics of soil leachate depending on the concentration of calcium chloride were as shown in Fig. 2. The acidity (pH) of soil leachate of Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 6.97, 6.12, 6.03, 5.54 and 5.28 respectively. As the concentration of calcium chloride increased, the level of pH decreased significantly. The pH level of soil, as the most important chemical property of soil, has a broad range from 3 to 9 (Shin et al., 2001). Cations in soil related to alkalinity include potassium, calcium, magnesium and sodium, and when a large amount of these cations are selectively absorbed by plants, hydrogen ions (H+) are relatively released into soil, accelerating the acidification of the soil (Park and Lee, 2010). Therefore, the reason that the higher the concentration of calcium chloride, the lower the pH level of soil leachate seems to be that the concentration of acidic ions increased as hydrogen ions (H+), acidic cations in the leachate of the soil, are substituted by calcium ions (Ca2+), alkaline cations (Jeong, 2006). In addition, as Pennisetum alopecuroides grew markedly, the absorption of cations such as K+ seemed to increase in the reproductive growth period and hydrogen ions (H+) also seemed to be released from its roots (E.M. Lee et al., 2017). Meanwhile, the electrical conductivity of soil leachate of Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 0.51 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm, 1.66 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm, 2.83 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm, 5.90 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm and 14.50 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm respectively. In addition, as the concentration of calcium chloride increased, the electrical conductivity of experimental groups statistically significantly increased compared to the control group. The difference that each experimental group showed compared to the control group was 1.15 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm, 2.32 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm, 5.39 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm and 13.99 ╬╝S ┬Ę cm respectively. Electrical conductivity is an indicator that shows the strength of electrolyte ions in soil leachate (Yi et al., 2012). The absorption mechanism of water and inorganic nutrients differ, and when calcium chloride solutions of different concentrations were injected, the amount of inorganic elements in the leachate of soil seems to increase, which in turn seems to gradually increase electrical conductivity (E.M. Lee et al., 2017). According to the landscaping design standards in Korea (Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture, 2013), when the electrical conductivity of soil is lower than 0.2, 0.2ŌĆō1.0, 1.0ŌĆō1.5, and 1.5 or higher, its grade is classified as good, medium, bad and poor respectively (Table 1). Both Cont. and C1 groups can be classified as good soil, and the C5 and C10 groups can be assessed as poor soil in terms of electrical conductivity. However, in terms of the width and number of leaves in the growth of plants, the values tended to increase also in the C5 and C10 groups, which indicates that Pennisetum alopecuroides as a salt tolerant plant can grow even in the soil of high electrical conductivity. In terms of the amount of exchangeable cations of salt in the calcium chloride solutions, the amount of K+ in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 18.42 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 42.01 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 42.99 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 44.45 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 and 107.03 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 respectively and that of Ca2+ was 13.68 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 100.58 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 275.86 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 692.15 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, and 1898.76 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 respectively. The amount of Na+ in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 46.26 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 81.71 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 102.21 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 116.77 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, and 228.58 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 respectively and that of Mg2+ was 3.99 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 40.05 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 57.11 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 75.85 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 and 126.53 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 respectively (Fig. 2). Overall, as the concentration of calcium chloride increased, the amount of Ca2+, Na+ and Mg2+ significantly increased, but the amount of K+ in the C1, C2 and C5 groups was relatively well maintained (42.01 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 42.99 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, 44.45 mg ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 respectively). It is important to control the cation and anions in the soil to an appropriate level because plants absorb the ions needed during their growth from the soil solution (Eom et al., 2019). When plants face a high level of salt stress, an ion imbalance occurs, and the inflow of Ca2+ and Na+ ions from outside seemed to increase affinity with K+ ions, accumulate a high concentration of K+ ions within the plant body, and reduce the inflow of Ca2+ and Na+ ions, which in turn seemed to maintain a certain level of K+ ions in the leachate of soil without any significant increase (Yun, 2005). Within the plant, K+ ion is one of the essential elements involved in Stomatal, Osmoconditioning, and photosynthesis (Eom et al., 2019). Stomata play an important role in the potential transpiration and photosynthesis of plants, prevent loss of moisture through the opening and closing of stomata and remove pollutants in the process of respiration through transpiration (Kim and Lee, 2017; Park and Lee, 2020). Therefore, Pennisetum alopecuroides will be effective in improving the soil of calcium chloride-damaged areas by suppressing the chloride K+ ion in the soil even at concentrations 5g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 of calcium chloride.
The growth response of Pennisetum alopecuroides depending on the concentration of a deicing material was as shown in Table 2. Height of plants in August when Pennisetum alopecuroides grows most markedly in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 96.82 cm, 110.13 cm, 103.33 cm, 95.11 cm and 78.55 cm respectively and the C1 group showed the highest value, followed by the C2, C5 and C10 groups, showing a significant decrease. The length of leaves in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 61.16 cm, 69.27 cm, 59.60 cm, 50.89 cm and 47.94 cm respectively and the C1 group also showed the highest value, while the value of the C10 group was lowest. The width of leaves in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 0.52 cm, 0.61 cm, 0.45 cm, 0.55 cm and 0.44 cm respectively. The C1 group showed the highest value, and the C10 group showed the lowest value, showing statistically significant differences. The number of leaves in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 25.37, 23.62, 22.25, 22.00 and 22.88 respectively. The Cont. group showed the highest value, and the C5 value showed the lowest value. However, the difference was not statistically significant. As a result, in terms of the growth response of Pennisetum alopecuroides depending on the concentration of calcium chloride, the C1 group showed the highest value all in the height of plants, the length of leaves and the width of leaves, and the concentration of calcium chloride was analyzed to have a slight impact on the height of plants and the length of leaves as the concentration was 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 or higher (Fig. 3). These results coincided with the results of Ju et al. (2019) that the external shape of Miscanthus sinensis treated with calcium chloride of 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 was maintained, but its growth decreased when the concentration was high (10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1). The growth response of plants is a good indicator for identifying the salt tolerance of plants, and many researchers have reported that the growth of plants was inhibited when the level of salinity was high (Scheiber et al., 2008). The mechanism of salt damage to plants is as follows. As the osmotic pressure in soil increases due to the excessive accumulation of salt, the suppressed absorption of water leads to moisture deficiency, the excessive absorption of certain ions, and thus the low growth of plants, which increases as the concentration of salt increases (Lee et al., 2007). Salt-tolerant plants, however, release from their body salt such as K+, Ca2+, Na+, M g2+ and ClŌłÆ or transfer salt into a salt pouch within their body to maintain their normal physiological activities (Zhao et al., 2011), and the characteristics of Pennisetum alopecuroides seemed to contribute to the good growth results even in the C5 group. Therefore, calcium chloride does not seem to affect the growth of Pennisetum alopecuroides until the concentration reaches 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, but the high concentration of 10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 seems to result in moisture deficiency and reduce the activity of roots, affecting the overall growth of Pennisetum alopecuroides in the early growth stage (S.H. Choi et al., 2004).
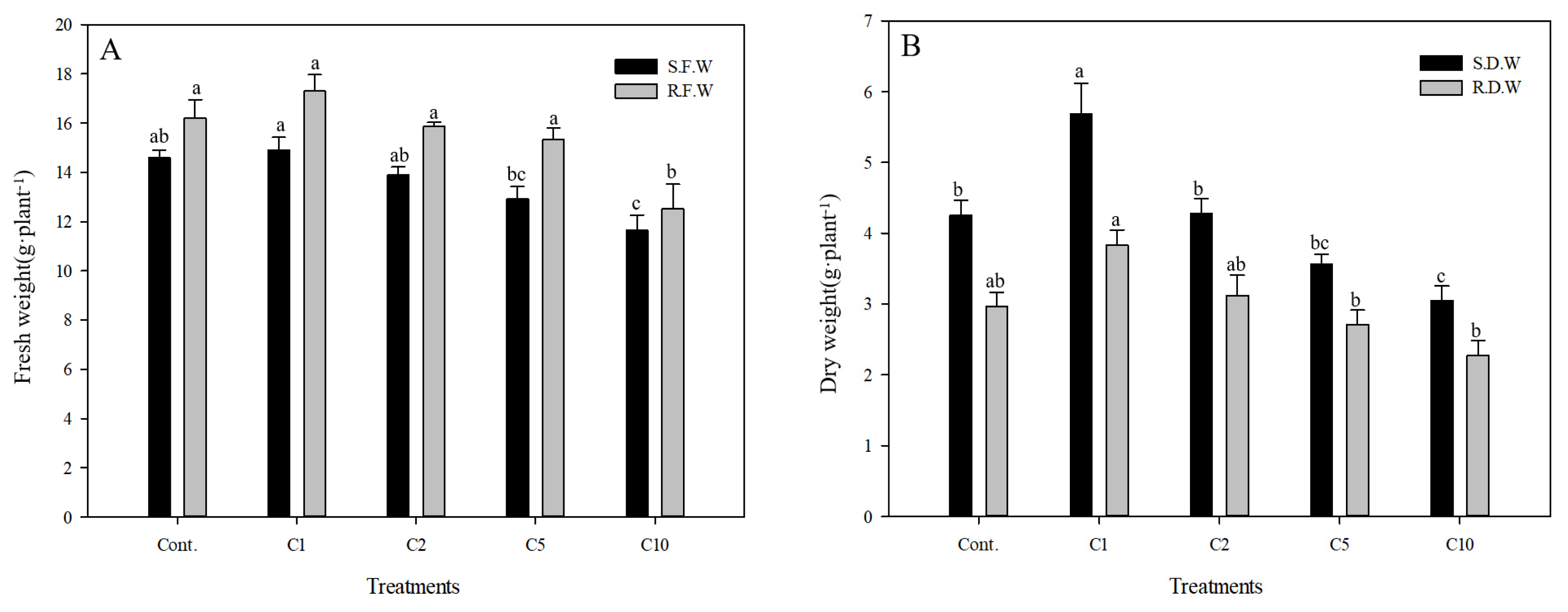
The fresh weight of the aerial part of Pennisetum alopecuroides in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was, similar to the results of growth, 14.59 g, 14.91 g, 13.90 g, 12.92 g and 11.65 g respectively, and the fresh weight was relatively well maintained until the concentration reached that of the C1 group, and started to reduce significantly from the concentration of 2 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (Fig. 4). The fresh weight of the underground part in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 16.20 g, 17.29 g, 15.87 g, 15.33 g, and 12.52 g respectively, and compared to the fresh weight of the aerial part, that of the underground part was higher. Compared to Cont. group, the fresh weight of the underground part in the C1 group was about 1.09g higher, showing the highest value. The dry weight of the aerial part of Pennisetum alopecuroides in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 4.25 g, 5.68 g, 4.28 g, 3.57 g and 3.05 g respectively, also showing the highest value in the C1 group. The value from the C2 group and higher tended to reduce significantly. The dry weight of the underground part in Cont., C1, C2, C5 and C10 groups was 2.96 g, 3.83 g, 3.12 g, 2.71 g and 2.27 g respectively, and the C1 group also showed a relatively high value. According to earlier studies, plants showed different growth responses to different containers, and it has been reported that rather than the size of containers the time and duration of the rhizosphere being constrained by the containers are more important. Since Pennisetum alopecuroides was grown in a green house where sufficient growth conditions including temperature, nutrients and water were provided in this study, the growth of Pennisetum alopecuroides progressed in August four months after it was planted and the 4-inch plastic pots (0.11 m ├Ś 0.9 m) did not seem to hinder the growth of roots in the rhizosphere (Seo et al., 2017). While the fresh and dry weight of Pennisetum alopecuroides tended to be significantly reduced as the concentration of calcium chloride increased, the C1 group was not significantly affected and showed an increase in the weight. There are 16 essential nutrients associated with the growth of plants, and according to the amount that the body of plants absorbs they are largely divided into macronutrients and micronutrients (Y.J. Lee et al., 2017). Chlorine (ClŌłÆ) as a micronutrient is accumulated in the body of plants due to its low mobility and increases the osmotic pressure of cells, and its hydrophile property also increases hydration in tissues. However, when chlorine is excessively accumulated in soil, it competitively inhibits the absorption of nitrogen, sulfur, phosphoric acid and boron that are absorbed by plants as an anion and also the growth of plants (Kim, 2000). Therefore, calcium chloride of 1 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 had a positive impact on the growth of plants, but the excessively accumulated chloride ions seemed to reduce water potential and thus to limit the growth of plants and to cause an imbalance in the absorption of ions, resulting in physiological side effects (S.C. Choi et al., 2004).
This study was conducted to identify the effects of Pennisetum alopecuroides on soil improvement in lands damaged by calcium chloride and its applicability as a greening plant. The growth response of Pennisetum alopecuroides and the leachate of soil depending on the concentration of calcium chloride were analyzed, and Pennisetum alopecuroides was found to maintain stable growth conditions in terms of the length of plants and the length and width of leaves when the concentration was 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1. The number of leaves was not affected even at the concentration of 10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1. After completing the experiment, the fresh and dry weight of the aerial and underground parts were measured, and they were highest when the concentration of calcium chloride was 1 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, and the fresh and dry weight of Pennisetum alopecuroides tended to decrease, showing statistically significant differences between different concentrations. In terms of the characteristics of soil leachate, as the concentration of calcium chloride increased, the level of pH decreased and the level of electrical conductivity increased significantly. Among exchangeable cations, the amount of K+ ions did not show any significant change until the concentration of calcium chloride reached 5 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, while Ca2+, Na+ and Mg2+ significantly increased. Given the results of the experiment, calcium chloride does not seem to affect the growth of Pennisetum alopecuroides until the concentration of calcium chloride reached 5g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1, but the concentration of 10 g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 or higher seems to inhibit its growth. As a plant that is relatively more tolerant to salt damage, Pennisetum alopecuroides was found to grow even in the soil damaged by deicing materials and planting Pennisetum alopecuroides can be highly utilized to improve the soil damaged by deicing materials by reducing the amount of K+, an exchangeable cation of salt. This study treated Pennisetum alopecuroides that can be introduced as a plant for the roadside with different concentrations of calcium chloride and the results are expected to be utilized in selecting plants for the lands damaged by deicing materials. However, since this experiment was conducted in a green house for one year using pots, it will be necessary to monitor and verify the results for a long term through an additional on-site experiment.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government(MSIT) (No. 2018R1A1A3A0).
Fig.┬Ā2
Electrical conductivity and acidity(A), and exchangeable cations(B) of collected leachates from pots of the different calcium chloride (CaCl2) concentrations; Non treatment (Cont.); CaCl2 1g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C1); CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C2); CaCl2 5g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C5); CaCl2 10g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C10). Vertical bars means present SEs (n = 18). Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by the different letters (p Ōēż .05).
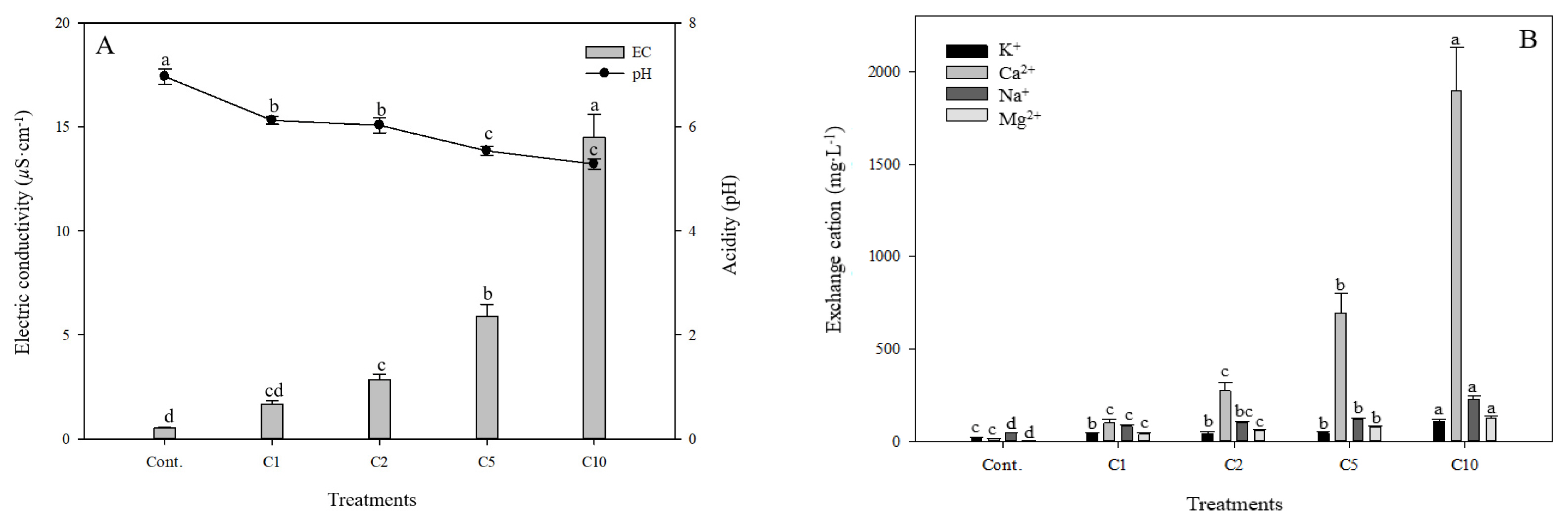
Fig.┬Ā3
Photo of Pennisetum alopecuroides grown as affected by calcium chloride (CaCl2) concentration. Non treatment (Cont.); CaCl2 1g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C1); CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C2); CaCl2 5g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C5); CaCl2 10g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C10) at 4 months after treatments.
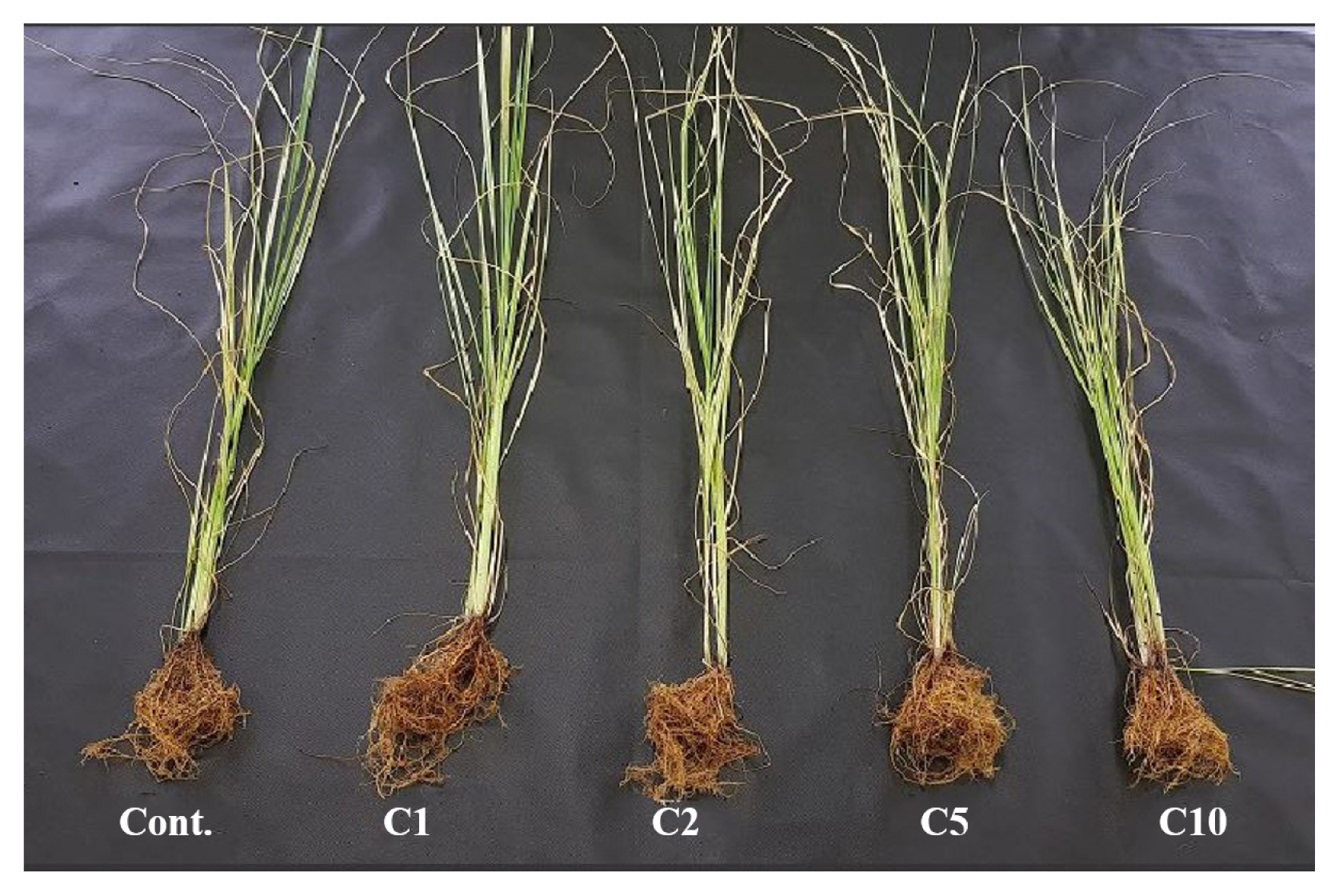

Fig.┬Ā4
Fresh weight(A) and dry weight(B) of Pennisetum alopecuroides as affected by calcium chloride (CaCl2) concentration; Non treatment (Cont.); CaCl2 1g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C1); CaCl2 2g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C2); CaCl2 5g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C5); CaCl2 10g ┬Ę LŌłÆ1 (C10), shoot fresh weight (S.F.W); shoot dry weight (S.D.W); root fresh weight (R.F.W); root dry weight (R.D.W). Vertical bars means present ┬▒ SEs (n=10). Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by the different letters (p Ōēż .05).
Table┬Ā1
Proper ranges of chemical properties of landscape soil
Note. Adapted from ŌĆ£Architectural Design Standards approved by Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs,ŌĆØ by Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture, 2013, Appendix table 7-2, Seoul, Kimoondang. pH=Acidity; E.C. =Electrical conductivity; Ex. K+=Exchangeable cation K+; Ex. Ca++= Exchangeable cation Ca2+; Ex. Mg++= Exchangeable cation Mg2+.
Table┬Ā2
Growth characteristics of the Pennisetum alopecuroides after treatment of different calcium chloride(CaCl2) concentrations
| Treatmentz | Plant height (cm) | Leaf length (cm) | Leaf width (cm) | Number of leaves (ea) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cont. | 96.82by | 61.16a | 0.52ab | 25.37a |
| C1 | 110.13a | 69.27a | 0.61a | 23.62a |
| C2 | 103.33ab | 59.60a | 0.45b | 22.25a |
| C5 | 95.11b | 50.89bc | 0.55a | 22.00a |
| C10 | 78.55c | 47.94c | 0.44b | 22.88a |
| F | 8.543 | 6.279 | 4.725 | 0.660 |
| p | < .001*** | .001*** | .003** | .624NS |
References
Beak, DW, WK Choi, SH Kang, GO Shin, SJ Park, CM Kim, HC Park, DJ Yun. 2014. Screening of salt-tolerance plants using transgenic Arabidopsis that express a salt cress cDNA library. J Plant Biotechnol. 41(2):81-88.
https://doi.org/10.5010/JPB.2014.41.2.81


Cho, SY 2003 Pre-wetted salt spreading. KSCE Mag 51(5):16-19. Retrieved from https://www.ksce.or.kr
.
Choi, SC, JJ Bae, YS Choo. 2004. Inorganic and organic solute pattern of costal plants, Korea. Korean J Ecol. 27(6):355-361.
https://doi.org/10.5141/JEFB.2004.27.6.355


Choi, SH, HI Kim, Y Ahn, JR Jang, JM Oh. 2004. Salinity effects in growth and yield components of rice. Korean J Limnol. 37(2):248-254.
Dang, JH, YH Cho, CS Lee. 2017. Effect of soil reinforcement on shear strength by Pennisetum alopecuroides and Miscanthus sinensis roots on loamy sand at river banks. J Korean Environ Restor Technol. 20(2):81-93.
https://doi.org/10.13087/kosert.2017.20.2.79

Eom, JY, K Pros, JS Lee, YG Kim, JW Park, JS Lee, GH Han. 2019;August;Distribution of potassium ion (K+) concentration in soil extraction solution according to farming type and soil characteristics. In: Proceedings of the International Academic Conference of Korean Society of Soil Science and Fertilizer; pp 89.
Gupta, B, B Huang. 2014. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int J Genom Advance online publication.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596


Jeong, JH, IS Han, SH Lee. 2001. Effects of several Korean native wild perennial flowers and kinds of basal sheets on sod formation. J Korean Environ Restor Reveg Technol. 4(4):19-24.
Jeong, MI, NR Jeong, WH Seung, JS Kim. 2020. Analyzing growth reactions of herbaceous plants for irrigation management. J People Plants Environ. 23(3):255-265.
https://doi.org/10.11628/ksppe.2020.23.3.255


Jeong, WK 2006 Understanding of soil acidity and management of acid soil. Soil Fert 25:29-35. Retrieved from http://www.ksssf.org
.
Ju, JH, J Yang, SY Park, YH Yoon. 2019. Effects of soil amendments and planting Miscanthus sinensis on salt reduction and growth improvement in substrate irrigated with high concentration of calcium chloride deicing salts. J Korean Environ Restor Technol. 22(6):15-25.
https://doi.org/10.13087/kosert.2019.22.6.15

Kim, DJ, JS Lee. 2017. Misconceptions and truths of morphological characteristics in plant stomata. J Life Sci. 27(2):241-246.
https://doi.org/10.5352/JLS.2017.27.2.241


Kim, KJ, MJ Kil, JS Song, EH Yoo, KC Son, SJ Kays. 2008. Efficiency of volatile formaldehyde removal by indoor plants: Contribution of aerial plant parts versus the root zone. J Am Soc Hortic Sci. 133(4):521-526.
https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.133.4.521

Korean Institute of Landscape Architecture. 2013. Architectural Design Standards approved by Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs Seoul, Korea: Kimoondang.
Lee, EM, SK Park, GJ Kim, BC Lee, HC Lee, YU Yun, SB Park, JM Choi. 2017. Changes in inorganic element concentrations of drained nutrient solution and leaves in compliance with numerical increment of fruiting node during hydroponic cultivation of cherry tomato. Protected Hort Plant Fac. 26(4):361-367.
https://doi.org/10.12791/KSBEC.2017.26.4.361

Lee, JJ, BJ Kim, IS Choi, JR Park, JM Oh. 2015;May;Evaluation of water purification ability using vegetation for water purification. In: Proceedings of the Korea Water Resources Association Conference; pp 551-555.
Lee, KB, JG Kang, J Li, DB Lee, CW Park, JD Kim. 2007. Evaluation of salt-tolerance plant for improving saline soil of reclaimed land. Korean J Soil Sci Fert. 40(3):173-180.
Lee, YJ, JK Sung, SB Lee, JE Lim, YS Song, DB Lee, SK Hong. 2017. Plant analysis methods for evaluating mineral nutrient. Korean J Soil Sci Fert. 50(2):93-99.
https://doi.org/10.7745/KJSSF.2017.50.2.093


Liu, L, D Guan, MR Peart. 2012. The morphological structure of leaves and the dust-retaining capability of afforested plants in urban Guangzhou, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 19(8):3440-3449.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0876-2



Park, HM, AK Lee. 2020. Efficiency of removal of indoor pollutants by Pistia stratiotes, Eichhornia crassipes and Hydrocotyle umbellata
. J People Plants Environ. 23(1):15-21.
https://doi.org/10.11628/ksppe.2020.23.1.15


Park, KJ, HJ Bang. 2015 Improvement of concrete highway-subsidiary structures design criteria considering the abnormal climate and snow removal. KSCE Mag 63(1):43-49. Retrieved from https://www.ksce.or.kr
.
Park, YH, CS Lee. 2010;July;Importance and supply needs of limestone fertilizer. In: Paper presented at the Seminar of Korean Society of Soil Sciences And Fertilizer; pp 1-110.
Scheiber, SM, D Sandrock, E Alvarez, MM Brennan. 2008. Effect of salt spray concentration on growth and appearance of ŌĆśGracillimusŌĆÖ maiden grass and ŌĆśHamelinŌĆÖ fountain grass. HortTechnology. 18(1):34-38.
https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTTECH.18.1.34

Seo, TC, SW An, SM Kim, CW Nam, H Chun, YC Kim, TK Kang, SW Kim, SG Jeon, KS Jang. 2017. Effect of the seedlings difference in cylindrical paper pot trays on initial root growth and yield of pepper. Protected Hort Plant Fac. 26(4):368-377.
https://doi.org/10.12791/KSBEC.2017.26.4.368

Shim, MS, YJ Kim, CH LEE, CH Shin. 2012. Salt tolerance of various native plants under salt stress. J Bio-Environ Control. 21(4):478-484.

Shim, SI, SK Lee, BH Kang. 1998. Screening of saline tolerant plants and development of biological monitoring technique for saline stress II. Responses of emergence and early growth of several crop species to saline stress. Korean J Environ Agric. 17(2):122-126.
Shin, JH, HR Heo, JS Shin, MY Kim, JY Shin. 2001. A study of effects on environment from road deicings. Korean J Sanit. 16(4):31-37.
Shin, SS, SD Park, HS Kim, KS Lee. 2010. Effect of calcium chloride and eco-friendly deicer on the plant growth. J Korean Soc Environ Eng. 32(5):487-498.
Son, DJ, KJ Kim, NR Jeong, HG Yun, SW Han, JH Kim, GR Do, SH Lee, CC Shagol. 2019. The impact of the morphological characteristics of leaves on particulate matter removal efficiency of plants. J People Plants Environ. 22(6):551-561.
https://doi.org/10.11628/ksppe.2019.22.6.551


Yi, YM, CT Oh, GJ Kim, CH Lee, KJ Sung. 2012. Changes in the physicochemical properties of soil according to soil remediation methods. J Soil Groundw Environ. 17(4):36-43.
https://doi.org/10.7857/JSGE.2012.17.4.036


Yun, DJ 2005. Molecular mechanism of plant adaption to high salinity. Korean J Plant Biotechnol. 32(1):1-14.


Zhao, K, J Song, G Feng, M Zhao, J Liu. 2011. Species, types, distribution, and economic potential of halophytes in China. Plant Soil. 342(1):495-509.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0470-7


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- 1,553 View
- 30 Download
- Related articles in J. People Plants Environ.