실내 관엽식물의 디자인 요소적 분류에 따른 선호도 및 감성 차이
Differences in the Preference and Emotion to Indoor Foliage Plant Grouped by the Type of Design Material
Article information
Abstract
The study was surveyed to 269 respondents for investigating psychological response to indoor foliage plants grouped by four type of design materials. 21 indoor foliage plants grouped as filler, mass, form, and line plant, are shown to each respondent for surveying the preference and emotion by SD (semantic differential) scale. It was statically significant that the filler plant group was the least preferred one between the indoor foliage plant and the preference of line plant group was the highest. In filler plant Scindapsus aureus is significantly favored, in mass plant Aglaonema crispum and Syngonium podophyllum, in form plant Ficus banghalensis in line plant Dracaena fragrans ‘Lemon Lime’, respectively. The green is the most preferred color of leaf and gray is the least one. When investigated on the major emotions felt with four types of indoor foliage plant with SD scale, filler plant felt as ‘Bright’, ‘Light’, ‘Pale’, mass plant ‘Warm’, ‘Sharp’, form plant ‘Simple’, ‘Luxurious’ and line plant ‘Sophisticated’, ‘Luxurious’, ‘Pleasant’, ‘Soft’ and ‘Fancy’, respectively. This result will be valuable when the indoor garden is designed with an indoor foliage plant.
I. 서론
2014년 서울의 평균 이산화질소 농도(10의 15승 molecules/cm2) 는 18.6으로 세계 5위로 나타났으며 공기 질이 서울보다 나쁜 도시 는 중국 베이징, 광저우(이상 19.9), 일본 도쿄(19.2), 미국 로스앤 젤레스(18.9) 등으로 알려졌다(WOW Korea Business News TV, 2016). 1989년 8월 미국 EPA(Environmental Protection Agency) 가 발표한 10개 공공건물의 실내공기질에 대한 보고서에 따르면, 900종 이상의 휘발성 유기화합물이 에너지절감형 신축 건물에서 발견되었고, 이 중 몇몇 화합물의 농도는 실내 평균농도의 100배가 넘었다(US. EPA, 1995). 따라서 1980년대 우주정거장 계획을 진 행하던 미국 항공우주국(NASA)은 좁은 우주선에서 우주비행사 들이 가급적 오래 생존할 수 있는 방안을 연구하여 1989년 공기정 화 능력이 탁월한 50종의 실내식물을 발표(The Segye Times, 2015)하였으며 식물을 이용한 실내공기정화 효과에 따른 연구들 이 지속적으로 진행되고 있다(Wood et al., 2002; Yoo et al., 2015). 중국으로부터 넘어오는 초미세먼지와 각종 휘발성 유기화 합물(volatile organic compounds: VOC)로 인해 우리 국민들의 건강상 위험이 우려되는 것이 현실이다(The Segye Times, 2015). 특히 실내거주시간이 많은 현대인들은 오염물질에 대한 노출이 심 해 아토피 피부염이나 천식, 안질환, 두통, 어지러움 등의 빌딩증후 군 현상을 호소하고 있으며(Weschler and Shields, 1997), 이와 같은 신체적 피해 증상뿐만 아니라 피로, 스트레스 등 정서적 영향 에 미치는 요인 중 환경적 요인으로 인한 피곤함, 탈진, 그리고 우 울 등과 같은 심리적 피해 증상이 나타나기도 한다(Kang et al., 2005). 이러한 스트레스는 정서적, 심리적, 생리학적으로 위협을 받는 상태에 반응하는 과정이다(Evans and Cohen, 1987). 그러나 실내에 배치된 식물은 거주자의 기분을 편안하게 만들어주며, 자연 이나 식물경관과 같은 시각적 자극은 녹색에서 느낄 수 있는 안정 감을 통해 스트레스 경감(Ulrich et al., 1991; Parsons et al., 1998), 또는 삶의 질적 향상에 매우 효과적이다(Son et al., 2003). 또한 시각을 통해 식물의 잎을 많이 접함으로써 우리 인간들은 환 경적인 효과 이외에도(Lee, 2006; Relf, 1992) 사회성, 인내심, 그 리고 정서증진효과도 얻게 해 준다(Lee, 2006). 따라서 그린인테 리어용 실내관엽식물에 대한 사용자의 선호도, 치유효과에 대한 인 식, 시각적으로 느끼는 이미지에 대한 감성 등 심리적 효과에 대한 객관적 조사, 분석이 필요하다.
이에 본 연구는 실내 관엽식물을 이용해 최근 정서적 폐해에 취 약함을 보이는 도심속 실내 거주자들의 직업에 따른 실내 관엽식물 효과에 대한 인식, 형태적 특성에 따라 분류한 4그룹(21종) 식물의 선호도 및 실내 관엽식물에 따른 인간의 감성차이에 대해 조사, 분 석하여 실내식물을 활용한 실내 정원 조성시 활용 가능한 사용분류 기준을 마련하고자 하였다.
II. 연구방법
1. 감성어휘 측정에 사용한 대상식물
실내 관엽식물에 대한 대상자들의 일반적인 느낌을 알아보기 위 하여 실시하였으며, 감성어휘 측정에 사용할 실내 관엽식물의 타 당성 있는 선정을 위해 국립원예특작과학원에서 발표된 ‘에코힐링 을 위한 실내공기정화식물’을 기준으로 잎이 관상 대상이 되고 형 태적 분류가 가능한 21종의 식물을 선정하였으며, 선정된 21종의 실내 관엽식물을 구매한 후 동일한 플라스틱 화분(∅25 × H18cm) 에 식재하여 본 설문에 사용하였다. 21종의 식물형태에 따른 분류 는 절화장식에서 꽃의 형태적 특성에 따라 분류된 4 가지 형태적 분류(filler flower, mass flower, form flower, line flower)를 기 준으로 관엽식물의 형태적 분류에 적용하여 4가지 형태적(filler plant, mass plant, form plant, line plant) 분류1)를 실시하였다. 또한 분류기준은 최근 구입이 용이하고 실내정원 조성시(컨테이 너) 실내 식물의 크기, 주지목과 부지목, 지피식물로 사용되는 빈도 도 적용하여 분류하였다(Fig. 1-4).

Indoor foliage plants used for the survey. A: Fittonia verschaffeltii; B: Peperomia clusiifolia; C: Pilea glauca; D: Selaginella martensii; E: Scindapsus aureus; F: Davallia mariesii.
2. 설문응답자 특성
실내 관엽식물에 대한 인식과 직업별 실내 관엽식물에 대한 치 유 효과 및 선호도, 실내 관엽식물의 형태적 분류에 따른 그룹별 감 성 차이를 알아보기 위해 2014년 9월 국립원예특작과학원에서 실 시한 도시농업 교육 참가 교육생 및 대한민국 도시농업박람회장 (대구자연과학고)의 관람객 및 참석자들 308명을 대상으로 실시 하였으며 부적합한 39개의 설문을 제외하고 269명의 설문을 분석 하였다(Fig. 1). 일반사항에 대해 빈도분석을 실시한 결과, 성별은 남자 70.6%, 여자 29.4%였고, 전문가 여부는 비전문가 84.3%, 전문 가 15.7%, 연령층은 20대 미만 27.6%, 50대 26.0%, 40대 19.3%, 60대 이상 13.8%, 30대 7.4%, 20대 5.9%순이었다. 또한 직업은 학생 32.5%, 주부 25.7%, 회사원 21.6%, 기타 9.7%, 전문직 6.7%, 자영업 3.8%순이었다.
3. 조사항목의 구성
설문조사 항목은 직업별 실내 관엽식물에 대한 치유효과, 실내 관엽식물의 잎 색채 및 식물의 선호도 그리고 일반사항으로 구성 하였다. 직업별 실내 관엽식물에 대한 치유효과는 Kim(2012)이 사용한 산림치유의 효과 척도를 실내 관엽식물의 상황에 맞게 조 정하여 사용하였다. 또한 각 문항은 4점 Likert 방식으로 응답하 도록 하였고, 가장 부정 1, 가장 긍정 4(전혀 그렇지 않다 ~ 매우 그렇다)로 등급을 정하였으며, Cronbach’s α값은 0.820으로 나 타났다.
4. 평가도구
1) 실내 관업식물의 이미지를 보고 느끼는 감성
어의구별척도법(semantic differential method: SD 법)은 인 간의 감성을 표현하는 형용사를 사용하여 인간의 감정을 측정하는 방법으로 Osgood et al.(1957)에 의해 개발되었으며 경관이나 감 정 평가 등에서 널리 사용하고 있다. 본 연구에서는 경관평가용 이 미지 형용사(Im, 2009)와 식물에 관계될 수 있는 감성어휘중 Jang et al.(2011)의 식물의 이미지에 대한 감성조사에 사용되었던 형 용사 감성어휘(14쌍)를 사용하였다. 형용사 감성어휘의 양극사이 를 5단계로 나누어 제시한 후 응답자로 하여금 가깝게 느끼는 정도 에 따라 답하도록 하였다(Jang, 2013; Jang et al., 2014, 2015, 2016).
2) 자료 통계 분석
연구에서 수집된 자료는 SPSS WIN 12.0(SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 이용하여 분석하였다. 측정도구의 신뢰도 분석은 Cronbach’s α를 산출하였다. 실내 관엽식물의 잎 색채 및 식물의 선호도, 형용사 감성어휘 SD법은 일원배치분산분석, 실내 관엽식 물에 대한 인구통계학적 변수는 빈도분석을 시행하였다.
III. 결과 및 고찰
1. 실내 관엽식물에 대한 심리적 효과의 직업별 차이
실내 관엽식물이 주는 치유 효과에 대한 인식에 대해 직업별로 분석한 결과(Table 1), 5개의 문항중 “실내 관엽식물은 공기정화 효과를 높여준다”, “실내 관엽식물은 심리적 안정 효과를 높여준 다”, “실내 관엽식물은 인체의 자연치유력을 높여준다”의 3문항에 서 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 나타냈다. 특히 “실내 관엽식물은 공 기정화효과를 높여준다”는 문항은 자영업자보다 회사원과 전문직 종사자가 공기정화 효과가 좋다고 생각하는 것으로 나타났으며 다 소 큰 차이를 보였다. 또한 “실내 관엽식물은 심리적 안정 효과를 높여준다”는 문항에서도 자영업자보다 회사원이 유의하게 높게 나타났으며 “실내 관엽식물은 인체의 자연치유력을 높여준다”는 문항에서도 자영업자보다 회사원, 주부, 기타, 전문직 종사자들이 높게 나타나 전반적으로 자영업자가 다른 직업군보다 실내 관엽식 물의 효과에 대한 인식이 낮은 것으로 볼 수 있었다. 이는 사무실 가 까이 도시림이 있는 곳에서 일하는 근무자들이 도시림조차 없는 곳 에서 일하는 근무자들보다 업무만족도는 더 높았고, 일에 대한 스 트레스는 덜 느끼는 것으로 나타났다는 Shin(2007)의 연구와 같이 전문직종사자나 회사원들이 공기정화 효과, 심리적 효과, 자연치 유력에 대한 인식이 높게 나타난 본 연구와 유사한 결과를 볼 수 있 으며 특히 직무 스트레스에 노출되어있는 회사원들의 실내식물에 대한 인식뿐 만 아니라 환경적, 심리적으로도 매우 유용할 것으로 생각된다.
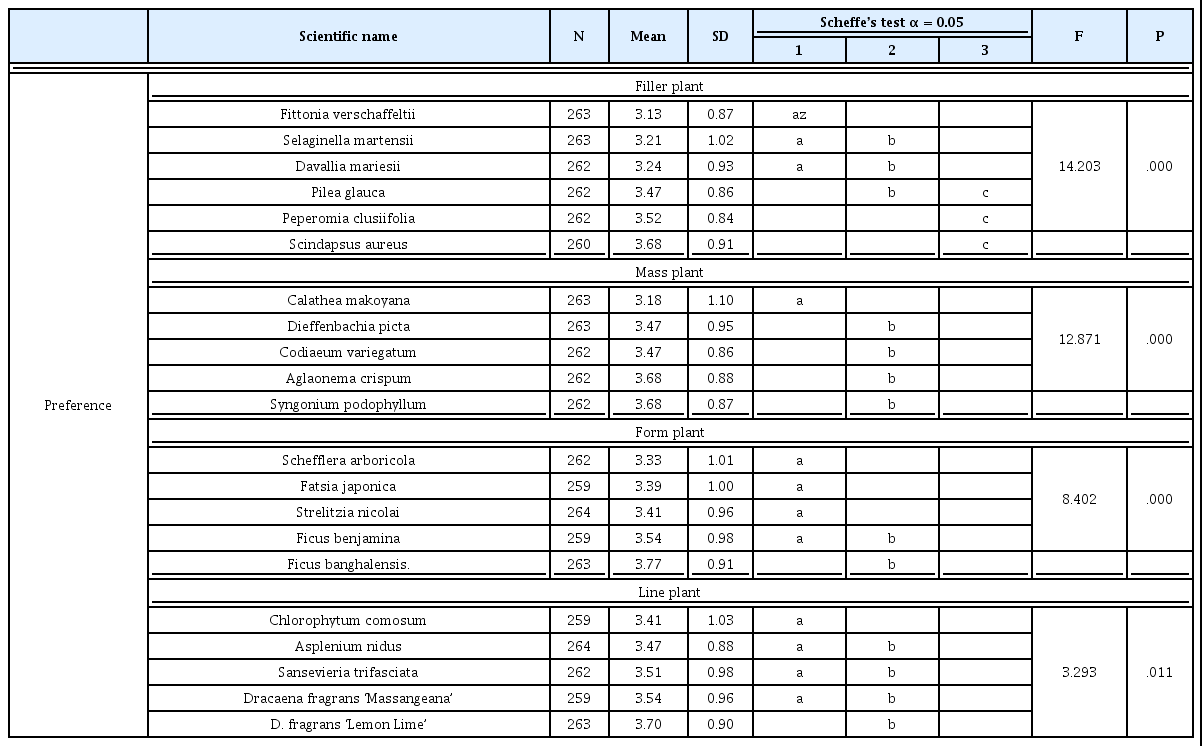
2. 21종류의 실내 관엽식물에 대한 선호도
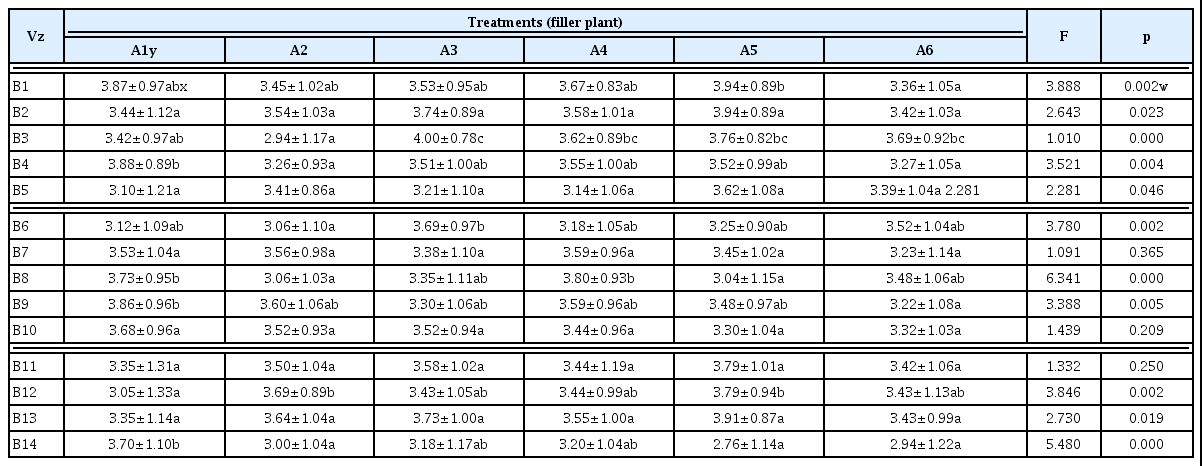
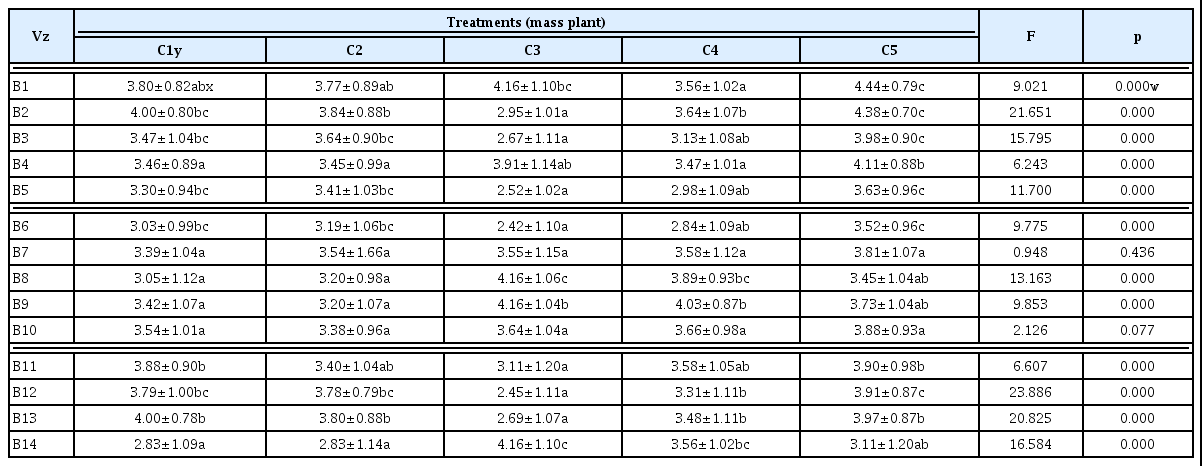
실내 관엽식물 21종류에 대한 선호도를 알아본 결과, F값은 9.497이고 유의확률은 0.000이므로 실내 관엽식물에 대한 선호도 는 통계적으로 유의한 것으로 볼 수 있었다. 21종류의 관엽식물중 벵갈고무나무의 선호도가 가장 높았고, 피토니아는 가장 선호도가 낮은 것으로 나타났다. 또한 실내 관엽식물 21종류의 식물을 4가지 형태적 특징을 기준으로 분류(filler, mass, form, line plant)한 식 물 그룹별 선호도를 알아보기 위해, Filler plant 그룹은 피토니아, 페페로미아, 타라, 부처손, 스킨답서스, 넉줄고사리(6종류), Mass plant 그룹은 싱고니움, 아글라오네마, 크로톤, 칼라데아, 디펜바 키아(5종류), Form plant 그룹은 벵갈고무나무, 큰잎극락조, 벤자 민고무나무, 대엽홍콩, 팔손이나무(5종류), 그리고 Line plant 그 룹은 산세베리아, 드라세나 레몬라임, 아스플레니움, 접란, 드라세 나 맛상게아나(5종류)로 분류된 그룹별 선호도(Table 2)를 알아본 결과, Filler plant 그룹은 스킨답서스의 선호도가 가장 높았고, 그 다음은 페페로미아 > 타라 > 넉줄고사리 > 부처손 > 피토니아순으 로 나타났다. Mass plant 그룹은 싱고니움, 아글라오네마 2종류의 식물의 선호도가 동일하게 가장 높았고, 그 다음은 크로톤 > 디펜바 키아 > 칼라데아순이었다. Form plant 그룹은 벵갈고무나무의 선 호도가 가장 높았고, 벤자민고무나무 > 큰잎극락조 > 팔손이나무 > 대엽홍콩순으로 선호하는 것으로 나타났다. Line plant 그룹은 드라세나 레몬라임을 가장 선호하였고, 드라세나 맛상게아나 > 산세베리아 > 아스플레니움 > 접란순으로 선호하는 것으로 나타 났다.
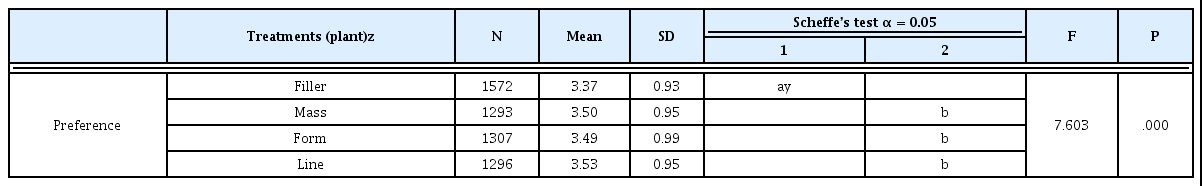
3. 실내 관엽식물의 4그룹간 선호도
실내 관엽식물의 4그룹간 선호도를 알아본 결과(Table 3), Line plant 그룹의 선호도가 가장 높은 것으로 나타났으며 Mass plant > Form plant > Filler plant순으로 Filler plant 그룹이 다른 3그룹보 다 통계적으로 유의하게 낮게 나타났다.
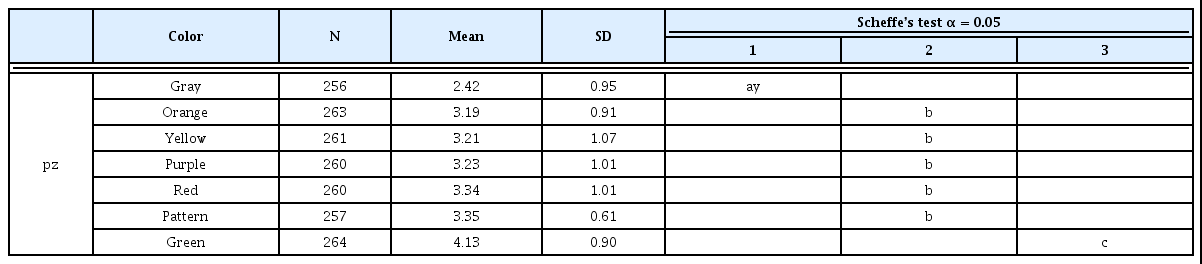
4. 실내 관엽식물의 잎에 대한 색채 선호도
그린인테리어어용 실내관엽식물 잎 색채에 대한 색채 선호도를 알아본 결과(Table 4), F값은 71.222이고 유의확률은 0.000이므 로 그린인테리어용 실내관엽식물 잎 색채에 대한 선호도는 유의한 것으로 볼 수 있었다. 선호도는 녹색이 가장 높았고, 무늬색 >적색 > 보라색 > 노란색 > 주황색 > 회색순으로 나타났다. 이는 절화장 식 색채 선호도 조사 결과, 녹색 절화 장식을 가장 선호하는 것으 로 나타났다는 Jang et al.(2016)의 연구, 업무공간에 식재된 실 내식물의 색채선호도가 녹색이 가장 높게 나타났다는 Ryou(2015) 의 연구는 녹색의 잎을 가장 선호하는 것으로 나타난 본 연구결과 와 유사한 경향이었다. 또한 색채와 감정은 연관관계가 있으며 특 히 녹색의 선호도가 높았다는 Ou et al.(2004)의 연구는 본 연구결 과와 같이 인간이 자연의 색과 가까운 녹색을 선호하는 것으로 해 석할 수 있다.
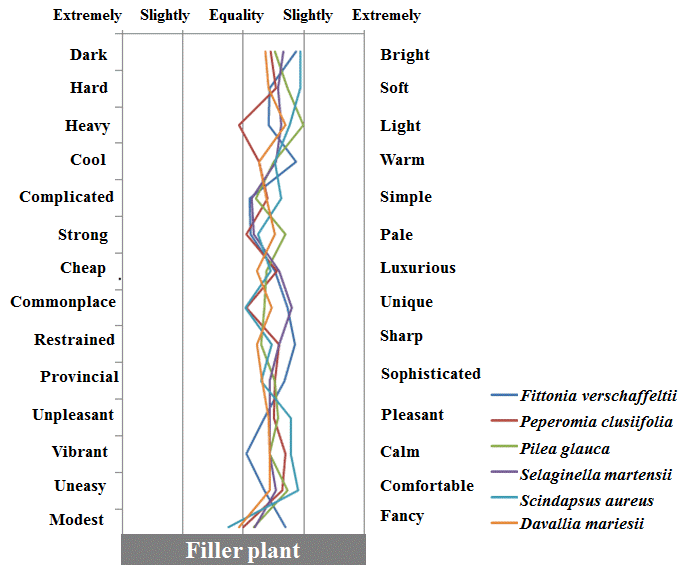
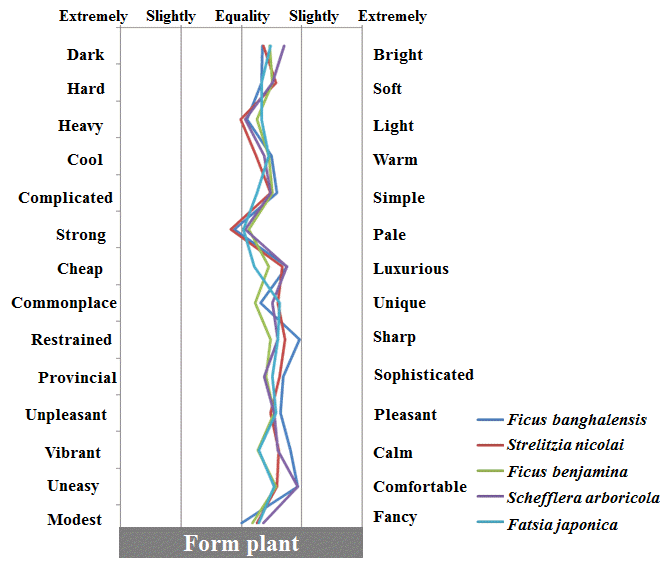
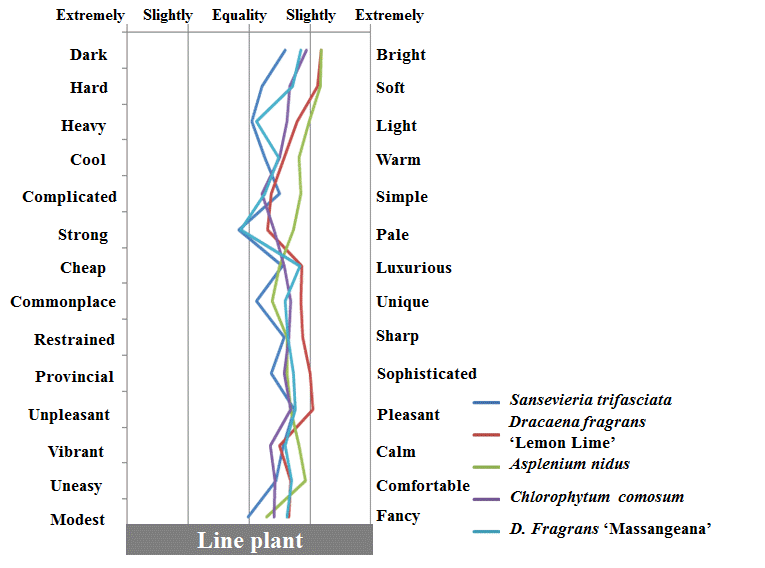
5. 실내 관엽식물에 대한 그룹간 대표 감성 차이
실내 관엽식물에 대한 4그룹간 대표되는 감성어휘를 알아본 결 과(Table 5), filler plant는 ‘밝은’, ‘가벼운’, ‘약한’ 감성, mass plant는 ‘부드러운’, ‘따뜻한’, ‘선명한’ 감성, form plant는 ‘단순 한’, ‘고급스러운’ 감성, 그리고 line plant는 ‘세련된’, ‘좋아하는’, ‘고급스러운’, ‘부드러운’, ‘화려한’ 감성을 각각 크게 느끼는 것으 로 나타났다.
6. 실내 관엽식물에 대한 그룹별 감성 심리설문 반응
1) Filler plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응
그린인테리어용 실내관엽식물의 filler plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응 결과(Fig. 5 and Table 6), 피토니아는 ‘따뜻한’, ‘선명 한’, ‘화려한’ 감성, 페페로미아는 ‘차분한’, ‘편안한’, ‘선명한’ 감 성, 타라는 ‘가벼운’, ‘부드러운’, ‘편안한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것 으로 나타났다. 또한 부처손은 ‘독특한’, ‘밝은’, ‘가벼운’ 감성, 스 킨답서스는 ‘밝은’, ‘부드러운’, ‘편안한’ 감성, 그리고 넉줄고사리 는 ‘가벼운’, ‘약한’, ‘독특한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났 다. 이는 실내조경디자인을 위한 공간 유형별 실내식물의 이미지 조사에서 스킨답서스가 ‘부드러운’ 감성을 크게 느끼는 것으로 나 타났다는 Yoo(2007)의 연구결과와 비슷한 결과가 도출되었다.
2) Mass plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응
그린인테리어용 실내관엽식물의 mass plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응 결과(Fig. 6 and Table 7), 싱고니움는 ‘부드러운’, ‘편안 한’, ‘좋아하는’ 감성, 아글라오네마는 ‘부드러운’, ‘차분한’, ‘편안 한’ 감성, 크로톤은 ‘독특한’, ‘선명한’, ‘화려한’ 감성 어휘 쪽이 높 은 것으로 나타났다. 또한 칼라데아는 ‘독특한’, ‘선명한’, ‘세련된’ 감성, 그리고 디펜바키아는 ‘밝은’, ‘부드러운’, ‘따뜻한’, ‘차분한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났다.
3) Form plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응
그린인테리어용 실내관엽식물의 form plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응 결과(Fig. 7 and Table 8), 벵갈고무나무는 ‘선명한’, ‘차 분한’, ‘편안한’ 감성, 큰잎극락조는 ‘세련된’, ‘고급스러운’, ‘부드 러운’ 감성, 벤자민고무나무는 ‘좋아하는’, ‘약한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 대엽홍콩은 ‘밝은’, ‘고급스러운’, ‘편안한’ 감성, 그리고 팔손이나무는 ‘독특한’, ‘선명한’, ‘좋아하는’ 감성어 휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났다.
4) Line plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응
그린인테리어용 실내관엽식물의 line plant 그룹에 대한 심리 설문 반응 결과(Fig. 8 and Table 9), 산세베리아는 ‘단순한’ 감 성, 드라세나 레몬라임은 ‘밝은’, ‘세련된’, ‘좋아하는’, ‘화려한’ 감성, 아스플레니움은 ‘부드러운’, ‘가벼운’, ‘차분한’, ‘편안한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 또한 접란은 ‘밝은’, ‘독특 한’ 감성, 그리고 드라세나 맛상게아나는 ‘고급스러운’, ‘좋아하 는’, ‘편안한’ 감성어휘 쪽이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 이는 실내식 물의 시각적 이미지가 주는 감성어휘 조사에서 맛상게아나에 대 해 ‘차분한’ 감성을 크게 느꼈다는 Jang et al.(2011)의 보고와 편 안한 느낌을 크게 받았다는 본 연구 결과와 유사한 경향으로 볼 수 있었다.
IV. 적요
본 연구는 실내 관엽식물에 대한 심리적 반응을 조사하기 위해 269명을 대상으로 설문조사하였다. 형태적 특성을 기준으로 분류 한 4그룹(filler, mass, form, line plant) 21종의 실내식물을 제시 한 후 식물선호도 및 어의구별척도법(SD법)에 따른 대표감성을 조 사하였다. 실내식물에 대한 그룹간 선호도는 Filler plant 그룹이 다른 3그룹보다 통계적으로 유의하게 낮게 나타났으며, Line plant 그룹의 선호도가 가장 높은 것으로 나타났다. 식물에 대한 그룹별 선호도는 Filler plant는 스킨답서스, Mass plant는 아글라오네마, 싱고니움, Form plant는 벵갈고무나무, 그리고 Line plant는 드라 세나 레몬라임이 통계적으로 유의하게 높았다. 실내식물 잎 색채에 대한 선호도는 녹색이 가장 높게, 회색이 가장 낮은 것으로 나타났 다. 또한 형태적 특성을 기준으로 구분된 4그룹의 실내식물에 대한 대표 감성을 SD(semantic differential)법으로 알아본 결과, filler plant는 ‘밝은’, ‘가벼운’, ‘약한’ 감성, mass plant는 ‘부드러운’, ‘따뜻한’, ‘선명한’ 감성, form plant는 ‘단순한’, ‘고급스러운’ 감 성, 그리고 line plant는 ‘세련된’, ‘좋아하는’, ‘고급스러운’, ‘부드 러운’, ‘화려한’ 감성을 각각 크게 느끼는 것으로 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 실내 관엽식물을 활용한 실내 정원 디자인시 유용할 것을 생각된다.
Notes
Filler plant(채움식물): 높이 15cm 이하, 작품의 하층부분의 마무리 및 식물 과 식물의 연결에 사용
Mass plant(덩어리 식물): 높이 20-60cm 정도, 독립수 가까이 또는 낮게 식 재하여 부피, 무게감을 살림, 잎의 생장속도가 유사하여 잎의 높이가 비슷하 게 생장하는 식물
Form plant(형태식물): 높이 80cm 이상, 독립수로서 실내정원 조성시 작품 골격의 주축이 됨
Line plant(선식물): 하나하나의 잎이 선모양인 것을 기준으로 함